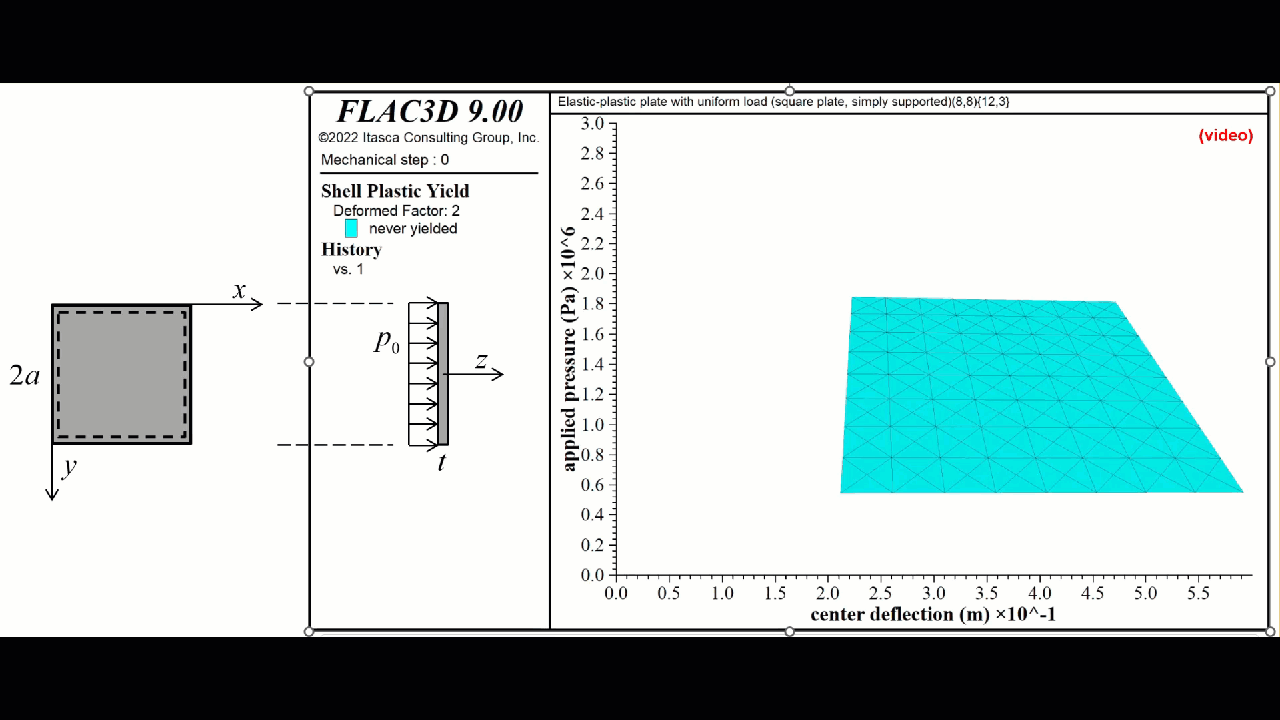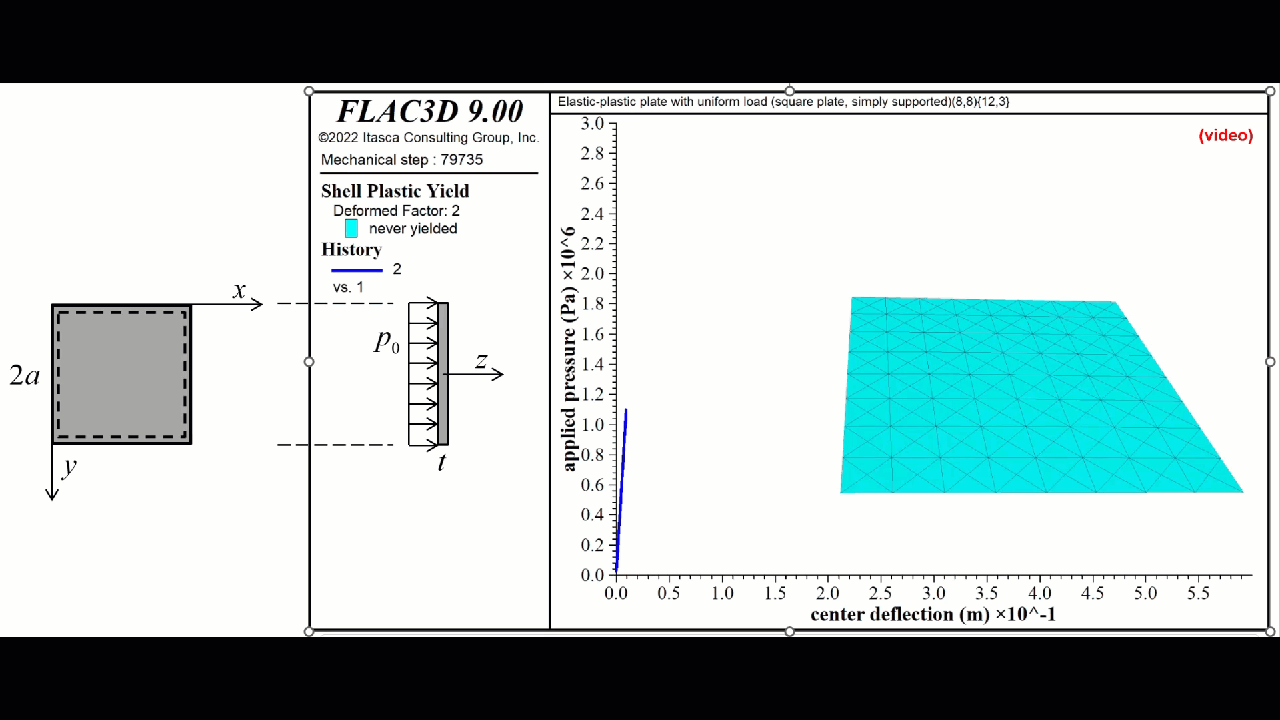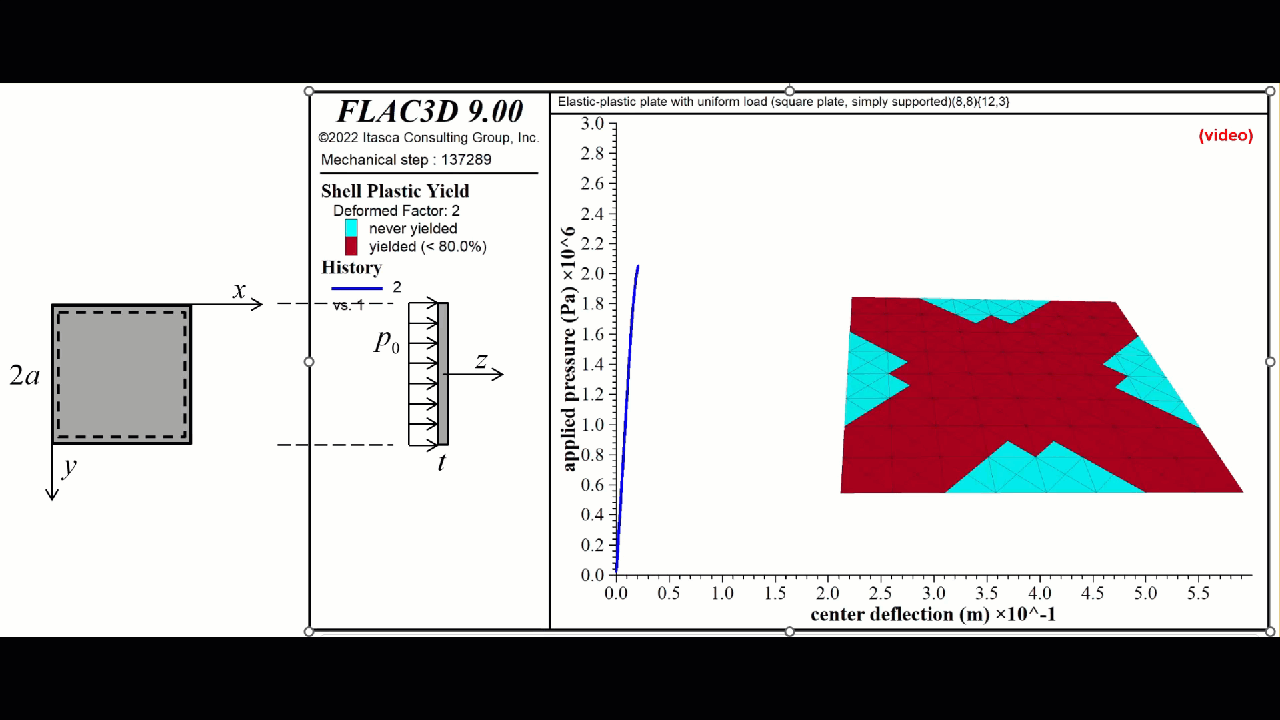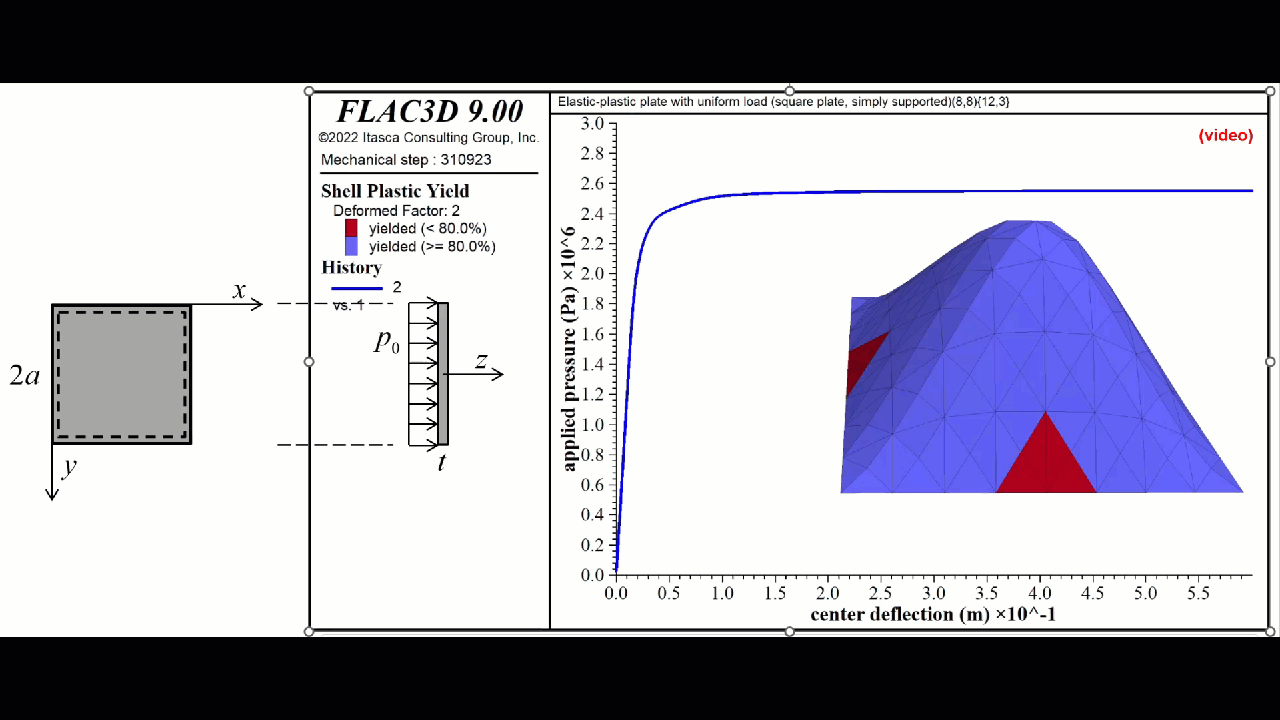
FLAC3D 9 introduces new non-linear structural elements for ground support for beams and piles/rockbolts and for shells, geogrids, and liners. Simple plastic hinges have been supplemented with a numerical integration scheme.
BEAM-TYPE STRUCTURES
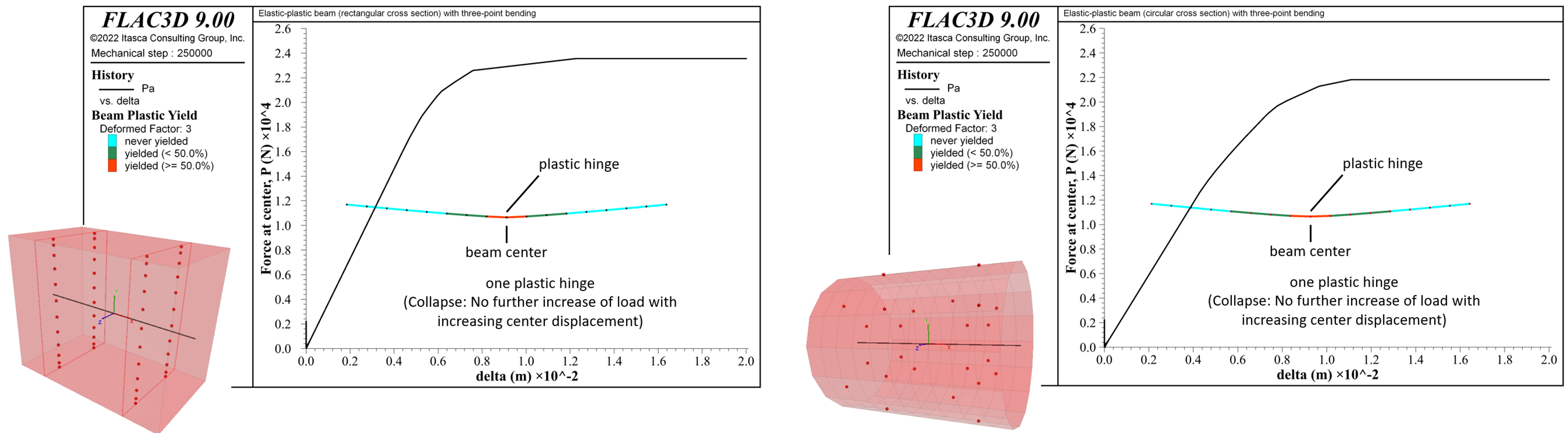
- The beam-type plastic constitutive models update the internal element forces by integrating the internal stress over the beam volume using a numerical integration scheme.
- The plasticity is induced by axial and bending deformations; twisting deformation induces an elastic response.
- The beam may have either a rectangular or circular cross section.
- Integration points are distributed throughout the volume of the beam elements.
- There are three beam plastic constitutive models, each of which is a one-dimensional version of the corresponding 3D model used by the zones:
- von Mises (steel beams)
- Mohr Coulomb (concrete beams)
- Strain Softening/Hardening Mohr Coulomb (concrete beams)
The following commands are for an rectangular cross-section aluminum ally beam:
struct beam cmodel assign von-mises
struct beam cmodel plastic-integration rectangular cross-section rectangular layout 3 5 3
struct beam property direction-y (0,1,0) young 68e9 poisson 0.33 strength-yield 270e6 modulus-plastic 0.0; 6061-T6 Al alloy
SHELL-TYPE STRUCTURES
- The plastic constitutive models update the internal element forces by integrating the internal stress over the shell volume using a numerical integration scheme.
- There are a group of integration points distributed throughout the volume of each shell element.
- There are three shell plastic constitutive models, each of which is a plane-stress version of the corresponding 3D model used by the zones:
- von Mises (steel shells)
- Mohr Coulomb (concrete shells)
- Strain Softening/Hardening Mohr Coulomb (concrete shells)
- Plasticity is provided by the DKT, CST and DKT-CST finite elements.